Super Elastic Alloy, the Earth's Orbit and Ice Ages and where did all the Carbon come from?
March 20
This week we investigate a super elastic alloy that will be very useful for future space travel. We discover a new sapphire based nano structure that soon cover our phones, windshields and provide new lenses for our glasses. We consider a new analysis of the Earth’s Orbit and its impact on Ice Ages. We even predict when the next Ice Age will occur. Finally we ponder where all the carbon on Earth initially came from. We know that all elements outside of Hydrogen and Helium are initially formed in stars so how did the carbon get here?
Super Elastic Alloy for Space Travel
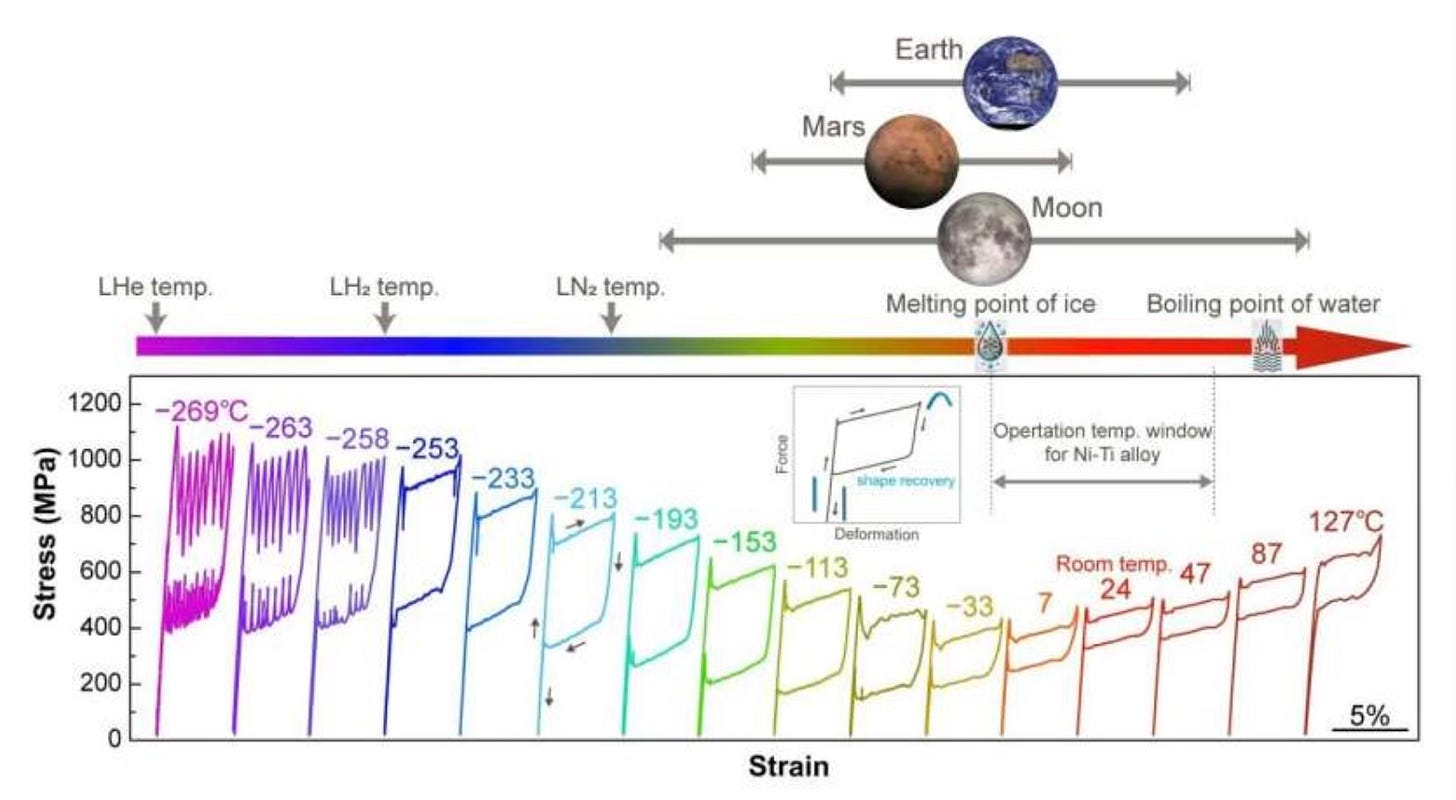
A team at Tohoku University have developed a lithium-aluminium based super elastic alloy that is lightweight and strong. The unique capability of this alloy is that it can function across a broad temperature range from as low as -269C (the temp of liquid helium) to 127C (above the boiling point of water).
Most current shape memory alloys (materials capable of regaining their original shape after force is removed) are limited to specific narrow temperature ranges. This new alloy operates in a vastly wider temperature range. This opens up applications in space travel and everyday medical tools. The discovery may also open up new material designs.
Sapphire Nano Structures
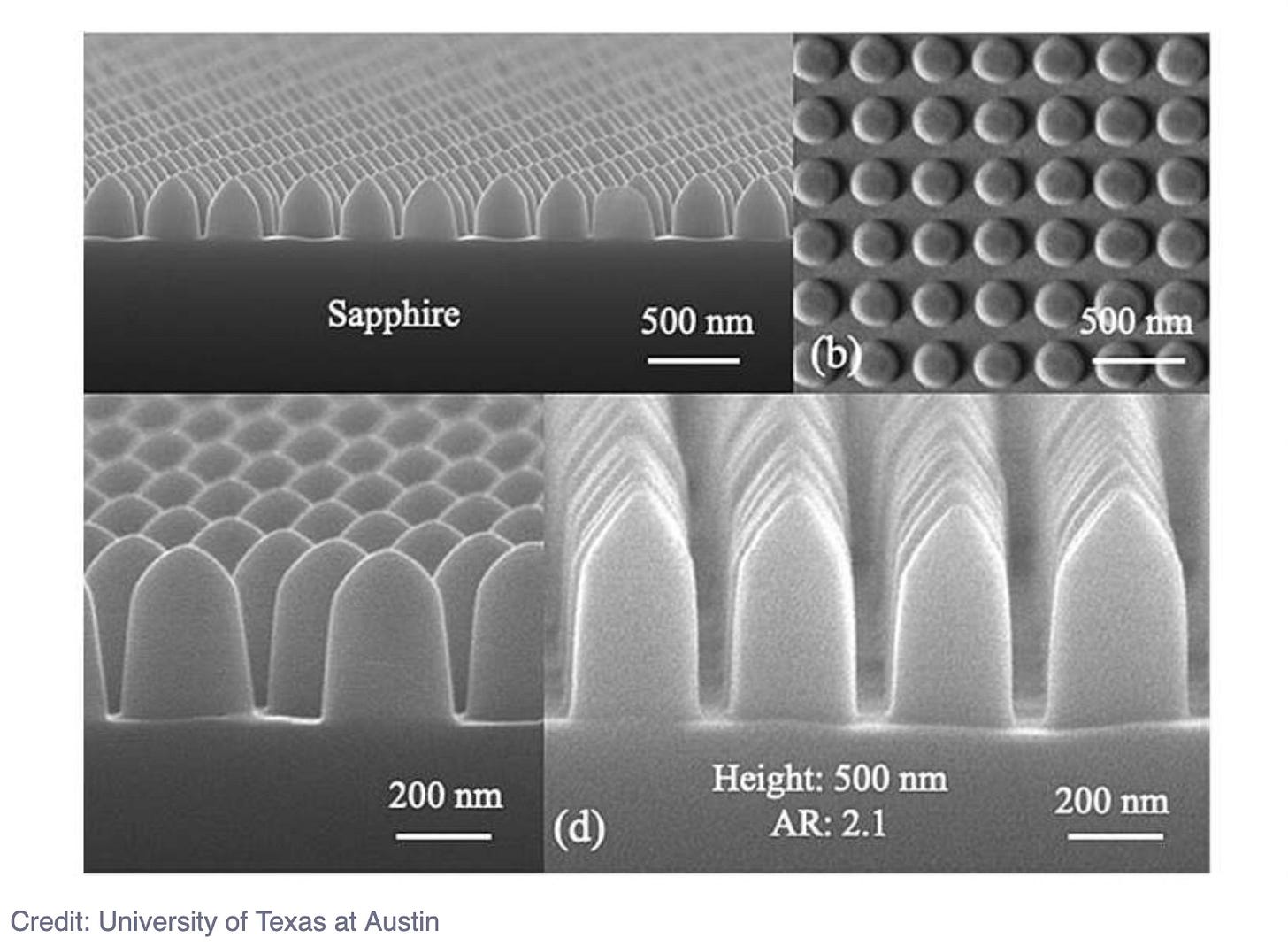
A team at University of Austin in Texas have developed a sapphire based material that could be part of a phone screen that can not be scratched, glasses the prevent glare and a windshield that will not get dusty.
Sapphire is more than a pretty stone. It is used extensively across defense, consumer electronics and next generation windows. It is nearly impossible to scratch. It is valuable due to its hardness and many other favorable properties however it is difficult to manufacture at small scales.
The team have been able to retain the strengths of sapphire without completely losing the stiffness and hardness. The new nano structures repel fog, dust and glare with self cleaning capabilities. Most nano structures are very fragile however using sapphire has solved this problem.
This new technology could lead to smartphones that are easier to read in challenging conditions, lenses and windows that do not fog up, cameras that are not prone to glare and hardy windshields that don’t get dusty. There are also applications in space travel (the moon is very dusty). The surface will remain 98.7% dust free using gravity alone.
Earth’s Orbit and Ice Ages
An International team based in University of California Santa Barbara have predicted when the next ice age will start. It has been 11,700 years since the last ice age and the team predicts that the next one will start in approximately 10,000 years.
The team analyzed a million year record of changes in our climate. This record is based upon the changes in size of land based ice sheets across the Northern Hemisphere and corresponding temperatures in the deep ocean. These changes were then matched with small cyclical variations in the shape of the Earths orbit of the sun, its wobble and the angle at which its axis is tilted.
A predictable pattern was found over the million year record matching the Earth’s climate changes between glacial ‘ice ages’ and warmer periods such as the one we are experiencing today. The pattern suggests that we are in the middle of a stable interglacial period called the Holocene (man made climate change may well disrupt that pattern).
The end of any ice age was found to be determined by a combination of changes in the wobble of the Earth’s axis and variances in the Earth’s tilt (called Obliquity). The Earth’s tilt varies between 22.1 degrees and 24.5 degrees over a 40,000 year period. It is currently 23.4 degrees. Wobbles in the Earth’s axis (known as Precession) were found to vary across roughly 21,000 years.
Additionally the shape of the Earth’s orbit can change slightly (from more elongated to less) which changes our distance from the sun (this variation is know as Eccentricity). The orbit varies over two cycles of 100,000 and 400,000 years. Currently summer in the Southern Hemisphere takes place when the Earth is at its’ closest point to the sun. In the future the Northern Hemisphere summer will be when the Earth is closest to the Sun.
The team also found that Obliquity (tilt of the earth) was the sole driver behind starting a new ice age. It is somewhat comforting to know that we have 10,000 years left of summer.
Where did all the Carbon on Earth come from?
We are a carbon based life form. Without carbon we would not exist. So where did all this carbon come from to allow the formation of life on Earth? Hydrogen and Helium are thought to have been created as a part of the big bang however all other elements only exist because they were forged in stars. When those stars died the elements were flung into the intergalactic never, never and somehow they found their way into our part of the universe.
A team in the US and Canada recently confirmed that carbon and other star formed atoms (i.e. most of them) don’t drift randomly in space until they chance upon a star system to inhabit. In the Milky Way and other similar galaxies that are still forming new stars, these rouge atoms take a circuitous journey. They circle their galaxy of origin on giant currents that extend into intergalactic space.
These currents are known as the circumgalactic medium. They resemble a giant conveyor belt that pushes material out and draws it back into the galactic interior. Gravity and other forces can then assemble these atoms into planets, moons, asteroids and comets. Sometimes even new stars are formed.
The carbon in our bodies most likely spent a significant amount of time outside of our galaxy (we have travelled far and wide, just not as coherent beings).
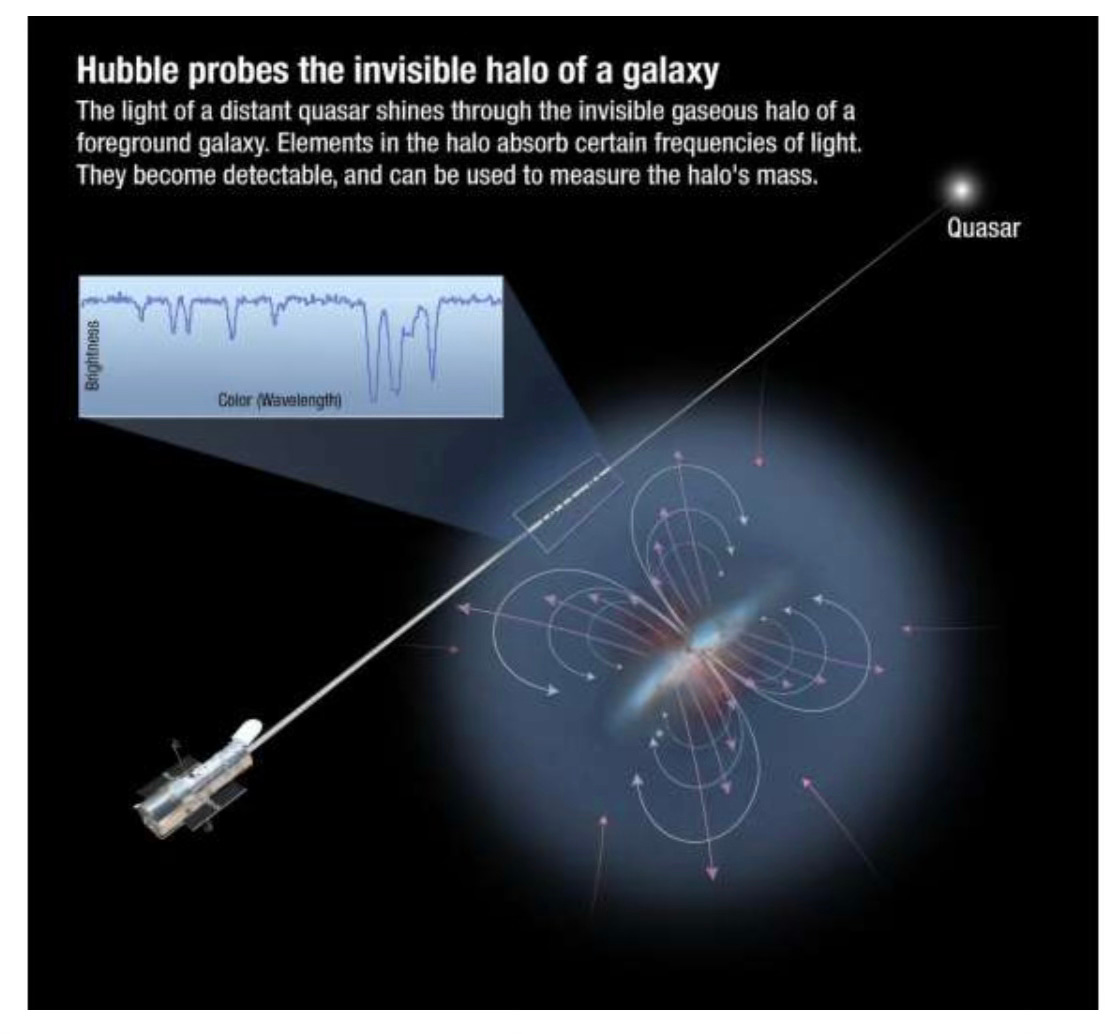
The circumgalactic medium was confirmed in 2011. This team confirmed for the first time that this medium also included carbon and oxygen. The team used a spectrograph on the Hubble space telescope to measure how light from nine distant quasars (ultra bright stars) is affected by the circumgalatic medium in 11 star forming galaxies.
The Hubble readings indicated that some of the light was being absorbed by a specific component in the circumgalactic medium i.e. carbon. They found lots and lots of it. Some carbon was detected 400,000 light years away from the Milky Way (that is four times the diameter of the Milky Way).
Future research will quantify the extent of other elements that make up the circumgalatic medium and compare the composition between different galaxies. All part of trying to understand how we got here.
Paying it Forward
If you have a start-up or know of a start-up that has a product ready for market please let me know. I would be happy to have a look and feature the startup in this newsletter. Also if any startups need introductions please get in touch and I will help where I can.
If you have any questions or comments please comment below.
I would also appreciate it if you could forward this newsletter to anyone that you think might be interested or provide a recommendation on Substack.