Converting heat from computing into electricity on the chip, have Google Simulated the Emergence of Life and a Periodic Table of Prime Numbers
July 18
This week we examine a new alloy that will allow the harvesting of heat energy given out by semiconductors whilst computing. We investigate Google’s claim that they have simulated the emergence of life. We look at a solar powered refrigerator truck and finally we discover a new Periodic Table of Prime numbers.
On Chip Energy Harvesting
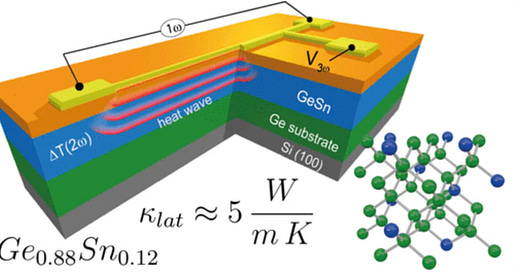
A team from Germany, Italy and the UK have developed a material suitable for harvesting the heat energy generated by computer chips. Composed of an alloy made of silicon, germanium and tin the thermoelectric material transfers the waste heat of computer processors back into electricity.
The researchers estimate that 1.2 exajoules of low temperature heat is wasted from IT infrastructure and devices in Europe each year. This equates to the energy production of Austria each year. This heat is below 80C and is challenging to harvest due to poor thermodynamic efficiency and technological constraints at that temperature.
The material converts heat into electrical energy where there is a temperature gradient from hot to cold across the material. It induces a flow of charge carriers generating electricity.
The material is compatible with the CMOS (Complimentary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) process of chip production so can be inserted into current systems. By integrating the new alloy into silicon based computer chips it is possible to ultilise waste heat generated during the operation and convert it back into electrical energy. This on chip harvesting could significantly reduce the need for external cooling and power.
The materials are all from Group IV materials (or silicon group materials). The ambitious goal to develop applications in thermo electronics, photonics and thermo electrics on the same chip. This will improve the performance of devices.
Google claims to have Simulated the Emergence of Life
The claim is not quite right but they have made a fascinating breakthrough. Google engineers set up a simulation to test what would happen if you left a bunch of random data alone for millions of generations.
When life first emerged on earth we think that it began is a primordial soup, a mixture of water and organic compounds. Over billions of years these particles had billions upon billions of tiny interactions and eventually the first organisms emerged. We don’t really know what this looked like but we postulate that from this chaos, order emerged in the form of life.
Google simulated the primordial soup with random data. The random data was a stand in for molecules. They imposed no rules on the system but used a programming language called “Brainfuck” to interact with the data. Brainfuck is the most minimalist programming system invented. It only allows two mathematical operations. Adding one or subtracting one when two pieces of data next to each other interact. Nothing else. The system then was allowed to interact in this way for billions of cycles.
The only thing data could do was interact with the piece of data next to it. Despite the primitive nature of the interactions, eventually self replicating programs developed. These programs were a type of digital lifeforms that could reproduce and continue to future generations.
The team claims that nothing magical happened, just physics. If you leave a chaotic system long enough to interact with itself some very complicated things will eventually emerge.
The emergence of self replication is a massive step forward to understanding how life emerged however it is not a simulation of the emergence of life. The system will need to show an increase in the complexity of organisms. The complexity increases substantially after the onset of self replication.
One day we may have enough computing power to set up a simulation large enough to show how life as we know it emerged. Of course there are some people that argue that this has already happened and we are the result of the that experiment by an even more intelligent life form. If you ever see pods of dolphins flying into the air and leaving the earth, you will know that they were correct (some of you will get that reference).
Solar Powered Freezer Truck
A team from Hong Kong Polytechnic University have developed a novel freezer truck that supports solar powered freezer systems and power storage and sharing.
There are currently 5,000 freezer trucks in Hong Kong. This number is growing rapidly. The vehicles are all powered by fuel engines, mostly diesel, which creates a significant pollution and noise problem in Hong Kong. The freezer system is powered by the vehicles internal combustion engine causing the engine to remain on when the vehicle is stationary. These freezers are kept at around -20C which limits the types of food that can be refrigerated.
The solar panels installed on the roof of an electric truck can be used to increase the truck’s power output enhancing energy efficiency. Additional energy storage allows the system to provide power for the freezer system. An onboard lithium ion battery can be recharged by standard electric vehicle charging systems. When the solar energy storage if full and the battery fully charged the freezer system can operate for up to 4 hours.
The onboard freezer system can maintain temperatures as low as -45C and will continue to operate after the engine is turned off. This turns the truck into a mobile freezer unit. The truck can connect to other vehicles of the same type allowing for energy sharing. The onboard smart energy management system allows users to optimize the freezer performance and prolong the life of the onboard battery.
The freezer truck is now ready for commercialization and it is expected that a range of similar vehicles will be launched in the near future.
Periodic Table of Prime Numbers
A team from City University of Hong Kong and North Carolina State University have upended hundreds of years of belief about prime numbers. Every mathematician has always claimed that prime numbers could not be predicted.
We have known for thousands of years that there are likely an infinite number of prime numbers, i.e. 1, 3, 5, 7, 11 etc which can only be divided by themselves and 1. We have always used trial and error to determine the next prime number. We just use more and more computing power to painstakingly try every number to determine if it is a prime number. The largest currently known prime number has 24,862048 digits. The prime number prior to this number has 23,249,425 digits. That is a lot of numbers that had to be tested before finding the current record holder (it took 5 years to find the current record). The occurrence of the next prime number has always appeared to occur randomly.
The team has worked out a way to predict accurately and swiftly when prime numbers will appear. They have created a periodic table of primes (PTP). The PTP can be used to shed light on finding a future prime, factoring an integer, visualizing an integer and its factors, identifying locations of twin primes, predicting the total number of primes and twin primes or estimating the maximum gap within an interval of primes.
Why is this useful? Prime numbers play a big part in encryption, cryptography and cyber security. Data can be made more secure if we can accurately predict new prime numbers. If anyone is interested the research paper can be found here.
Paying it Forward
If you have a start-up or know of a start-up that has a product ready for market please let me know. I would be happy to have a look and feature the startup in this newsletter. Also if any startups need introductions please get in touch and I will help where I can.
If you have any questions or comments please comment below.
I would also appreciate it if you could forward this newsletter to anyone that you think might be interested.
Till next week.